Diabetes
This information is sourced from Natural Cures. Rife and Zapper frequencies are at the end of this article.
Overview?
Diabetes (diabetes mellitus) is a chronic, degenerative disease caused by insulin deficiencies due to the body being incapable of producing normal insulin levels, or insulin resistance, a condition in which the cells of the body resist insulin’s attempts at regulating blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas to metabolize glucose, a form of sugar that is one of the primary sources of cells’ energy supply. Whether diabetes is caused by insulin resistance or a lack of insulin, the end result in the same: the body is unable to transport enough glucose from the bloodstream into the cells, especially after meals, when blood sugar levels rise as a natural consequence of digestion.??
Normally, blood sugar levels in the body are maintained by the body`s self-regulating mechanisms, known as homeostasis. A rise in blood glucose after eating is supposed to stimulate production of the hormone insulin in the pancreas, and the insulin released into the bloodstream should keep blood sugar levels within a safe and usable range. But when the insulin-producing cells of the pancreas are not functioning normally, glucose levels remain high. If this situation becomes chronic, the stage is set for diabetes to occur.
Diabetes affects tens of millions of Americans, and it is estimated that a third of all people who have diabetes are unaware of their condition. Diabetes accounts for nearly ten percent of all U.S. deaths for people 25 and older. It is also the main cause of new cases of blindness among adults 20 to 74 years old, and it is the leading cause of end-stage renal (kidney) disease. In addition, diabetes is the primary reason for amputations of the limb, and is a leading cause of heart disease.
Testing for Diabetes
Diabetes is generally tested for by measuring the amount of glucose in the bloodstream. There are three types of tests that can be used for this purpose. One is a direct measurement of blood glucose levels after an overnight fast, and the second is a measurement of the body’s ability to handle excess sugar after drinking liquid glucose. A third test method, the glycosylated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) test, measures the number of glucose molecules attached to hemoglobin over a period of two to three months.
The conventional “gold standard” for diagnosis of diabetes is a recurring elevated blood sugar level after an overnight fast. A fasting blood sugar value above 126 mg/dl on at least two separate occasions is said to be indicative of diabetes (whereas normal values are between 64 and 110 mg/dl). However, neither glucose metabolism problems, nor the early stages of Type II diabetes can be easily diagnosed without a 4 to 5 hour Glucose Tolerance Test that checks both glucose and insulin levels.
The goal of diabetic treatment is to restore near-euglycemia (blood sugar levels close to normal range) and to correct related metabolic disorders. Successful treatment requires diabetics to be actively involved in managing their special dietary and lifestyle needs. While insulin-dependent (Type I) diabetics have to be very diligent in the caring of the disease, we can expect diabetics to be successfully treated with diet, nutrition, stress management, exercise, detoxification, and herbs in about 95 percent of all diabetes cases.
Types of Diabetes
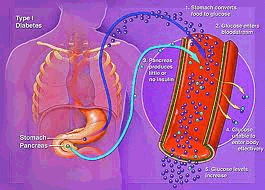
There are two main types of diabetes: insulin-dependent juvenile diabetes, or Type I diabetes, and non-insulin dependent diabetes, more commonly known as Type II diabetes. Both Type I and Type II diabetes are characterized by chronic high blood sugar levels, as well as other disturbances in carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism. Type II diabetes is by far the most prevalent form of diabetes, accounting for between 90 and 95 percent of all diabetes cases in the United States. People with Type I diabetes do not produce enough insulin, or do not produce any insulin at all in their pancreatic islet cells due to beta cell failure or destruction. In Type I diabetes, blood sugar rises because little or no insulin enters the bloodstream. Because insulin is needed to metabolize the sugars, the body’s cells cannot get the nourishment they need from glucose and the excess glucose just builds up in the bloodstream. Some glucose may be converted into fat, but most spills out into the urine. Type I diabetes usually begins in childhood (juvenile onset), but it may also occur later in life if the pancreas is damaged because of disease or injury. It is conventionally considered a degenerative condition and is treated (but not cured) by conventional physicians by administering insulin injections with every meal to regulate blood sugar.
Type II diabetes is much more common than Type I diabetes and is often called “insulin resistance.” In cases of Type II diabetes, the body still produces insulin, but the insulin it produces cannot properly connect with fat and muscles to allow glucose inside the cells to produce energy. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) an epidemic of adult-onset Type II diabetes is occurring around the world. Cases of Type II diabetes are increasing due to factors such as poor diet, obesity, sedentary lifestyles, and longer life spans.
Gestational Diabetes is yet a third type of diabetes. It is hormonally-triggered and usually a temporary condition that occurs in pregnant women. Gestational Diabetes is generally a mild condition, and more often than not is manageable through proper diet and exercise. Only rarely does it require insulin injections. Despite its typically temporary nature, gestational diabetes should be carefully addressed because high blood sugar levels can be damaging to the fetus and can impair the baby’s immune defenses.
Symptoms of Diabetes ?Classic symptoms of Type I diabetes are excessive thirst, excessive urination, excessive hunger, unhealthy weight loss, dehydration, and fatigue. Other complications that can result from unmanaged Type I diabetes are ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma. Ketoacidosis is a dangerous state of chronic acidity in the body, which means an acidic pH level. It occurs when the body breaks down fats for energy because it cannot get enough glucose. Acidosis results from the presence of ketones, the toxic byproducts of this reaction.
Caution: Ketoacidosis can be life-threatening and should be treated as a medical emergency. Hyperosmolar coma is also a life-threatening medical emergency that is fatal in about 50 percent of all cases and always requires hospitalization. It results from severe dehydration caused by low fluid intake, high blood sugar levels, and/or physical stress such as surgery or infection. Overall, the symptoms of Type II diabetes are the same as Type I, with the exception of unhealthy weight loss.
It is important to note that with Type II diabetics one will often experience excessive weight gain. Because the incidence of Type II diabetes is on the rise and often undiagnosed early on, it is important to monitor yourself for tell-tale signs that you might be at risk. This is especially true if, as you age, you also find yourself gaining weight, a possible indicator that you are developing a greater risk of insulin resistance.
Warning signs for the onset of Type II diabetes include carbohydrate cravings, bouts of dizziness, irritability, and progressive weight gain (especially around the abdomen), an increase in blood triglycerides and cholesterol levels, a progressive increase in blood pressure, fatigue after an “allergic” meal, fainting episodes, and frequent fungal infections. If you find yourself experiencing these symptoms, seek prompt medical attention. The chronic high levels of blood glucose that cause diabetes can lead to a variety of serious health conditions. Excess glucose in the bloodstream alters normal metabolic and biological functions. For example, it reduces the effectiveness of important proteins such as hemoglobin, the molecule that carries oxygen in red blood cells.
Research also shows diabetes can lead to increased quantities of very-low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, or the “bad” cholesterol. This occurs because excess glucose in the bloodstream gets transformed into fats, which in turn can lead to small arteries becoming narrowed by plaque. The end result, if left untreated, is very often high blood pressure and cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke. People with diabetes are three to four times more likely to die of heart attacks than people without diabetes who have the same number of other major risk factors.
Over the long term, elevated blood glucose levels can also cause damage to the kidneys (neuropathy, chronic renal failure); insufficient blood supply to the eyes (cataracts, retinopathy, glaucoma); other vascular system and organ damage; gastroparesis (loss of peristaltic action in the gastrointestinal tract); high risk of infection; and even death. In addition, poor circulation and peripheral nerve damage, both of which are commonly associated with diabetes, can lead to loss of sensation, neuropathy, foot ulcers, and potentially foot or leg amputation due to gangrenous infections.
Causes of DiabetesType I
Type I diabetes occurs because the pancreatic islet cells do not produce enough insulin, or no insulin at all, due to beta cell failure or destruction. In many cases, this is due to genetic predisposition, since Type I diabetes occurs more frequently among individuals who have inherited the tendency from parents. Many cases of Type I diabetes, however, are due to an autoimmune disease, as shown by the fact that 75 percent of Type I diabetics have antibodies to their own pancreatic cells, whereas only 0.5 percent to 2.0 percent of non-diabetics exhibit these antibodies. Among the factors that can initiate the destructive pancreatic autoimmune process are bacteria infections, especially pertussis (whooping cough), and viruses such as Epstein-Barr (EBV), Coxsackie, cytomegalovirus (CMV), and herpes virus-6, as well as viruses that cause rubella and hepatitis.
Bovine protein albumin, a substance contained in cow’s milk, can also trigger insulin-dependent diabetes by provoking an autoimmune response. Albumin antibodies found in some Type I diabetics can interfere with the insulin-producing pancreatic cells.
Type II
Poor diet, obesity, chronic food allergies, viral infections, chronic stress and genetic factors can all cause or contribute to Type II diabetes, which is primarily characterized by insulin resistance. The more insulin-resistant a person becomes, the more insulin the person`s body manufactures, yet, over time, the body becomes unable to produce enough insulin to make up for the resistance. Sometimes the Type II diabetic’s body will try to compensate, at least initially, by over-producing insulin. But over-production of insulin (a condition known as hyperinsulinemia) can cause damage to blood vessels and can also cause the liver to increase its output of LDL cholesterol, which is linked to the increased risk of heart disease.
??In recent years, obesity has become one of the most significant causes of Type II diabetes. Today, approximately 85 percent of people diagnosed with Type II diabetes are also excessively overweight. In fact, researchers now say it is basically inevitable that a person who is 30 percent overweight for 30 or more years will develop Type II diabetes. ??A diet that lacks essential nutrients and is high in sugar or foods that turn into sugar is the other major contributing factor to blood sugar metabolism problems and eventual insulin resistance. This has been documented by international researchers reporting about the increasing incidence of diabetes among populations around the world who adopt a “modern Western” diet high in sugar, carbohydrates, and fat.
Poor diet and lack of movement are also two of the primary factors causing excessive weight gain and obesity, further increasingly the likelihood of Type II diabetes. Without changing your diet, given the odds, the risk of diabetes is incredibly high. Other factors that can cause or contribute to the onset of Type II diabetes include viral infections, parasites, food allergies, and hormonal imbalances, including increased levels of adrenaline and cortisol caused by chronic stress. Certain allergies and viral infections can also cause inflammation or autoimmune damage to the insulin-producing pancreatic cells. Higher levels of stress hormones increase the risk of diabetes by stimulating elevated levels of sugar in the blood.
Excessive levels of the hormone estrogen also increase insulin resistance.??
Note: According to Daniel Dunphy, PAC, a holistic health practitioner at the Clear Clinic in Mill Valley, California who has achieved great success in treating diabetes, both Type I and Type II diabetes can often be caused by various harmful microorganisms and/or energetic imbalances that remain undetected by conventional medical testing. ?
Natural Cures for diabetes
Because Type I diabetes is so often due to hereditary factors, it is difficult to take preventive measures, yet there is much that can be done to prevent Type II diabetes, which is by far the most common form of diabetes. Adults who have a high-risk of Type II diabetes can prevent or delay its onset through lifestyle changes that include proper diet, high quality nutritional supplementation, stress reduction, and exercise.
Once one’s diet has improved, cleansing and detoxification techniques can be utilized to further improve health. If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, controlling your glucose levels is of primary importance in preventing or delaying complications. You will also need to control high blood pressure and to lower high cholesterol and triglyceride levels. In addition, you should seek alternative professional care for detecting problems in eyes, heart, kidneys, and feet.
Laser eye therapy can reduce the development of severe vision loss by more than 50 percent.
Proper foot care can reduce amputation rates by 45 percent to 85 percent.
And the early detection and treatment of kidney disease can reduce the development of kidney failure from 30 to 70 percent.
You also need to learn what constitutes good self-care and practice it diligently. The following natural cure approaches are very important in that regard.
Aromatherapy: The essential oils of cedar, olive or juniper can provide symptom relief when massaged into the lower left side of the body, where the spleen and pancreas are located.??
Ayurvedic Medicine: Ayurvedic approaches to controlling diabetes incorporate diet modification, including the elimination of sugar, simple carbohydrates, and a reduction of fats and overall protein intake. This helps one to avoid kidney damage.
Exercise, herbal medicine, and cleansing programs are key factors with the Ayurvedic approach. One Ayurvedic method is called pancha karma, which involves herbal massages and herbal steam saunas followed by fasting to cleanse the body. Sometimes herbal enemas and/or colonics are also employed. Cleansing programs are especially helpful when diabetes exists because of an autoimmune disease, which creates auto-antibodies that attack the pancreas. The herb Gymnema sylvestre is widely used by Ayurvedic physicians to stimulate the pancreas to produce insulin and to also block sugar absorption from the gut.
Other useful Ayurvedic herbs include bitter melon and neem, both of which lower blood sugar, stimulate the pancreas, and act as a liver tonic that helps prevent the formation of gallstones, a common symptom of many Type II diabetic patients.
Chelation Therapy: Chelation therapy is often very useful for preventing complications caused by diabetes. According to Garry F. Gordon, M.D., D.O., co-founder of the American College of Advancement in Medicine and developer of the modern-day chelation protocol, the benefits of EDTA chelation therapy include fewer cases of blindness and kidney dialysis, and a smaller number of amputations and other complications.
Deferoxamine chelation therapy has also been shown effective for reducing adult-onset diabetes. Deferoxamine is a chelation agent that effectively chelates excess iron out of the bloodstream. Recent studies have shown that women with high levels of iron triple their risk for diabetes.
Diet: Proper diet is critical for both preventing and treating diabetes, especially Type II diabetes. One of the most important dietary precautions you can take is to eliminate all refined sugars and sugar products from your diet. Such products include refined sugar, corn syrup, cornstarch, dextrose, dextrin, fructose, fruit juice concentrates, glucose, lactose, malt, maltodextrin, maltose, mannitol, sorbitol, sorghum, sucrose, and xylitol. Honey, Maple syrup, Agaves or Chicory syrup must also be eliminated if you are pre-diabetic or diabetic.
Also reduce or eliminate your intake of alcohol and caffeine. Remove fast food, refined foods, processed “junk” foods, soda, fried foods, and all products containing white flour. Choose quality protein snacks between meals, or soaked nuts, and fresh vegetables and vegetable only juices as between meal options. ?? To help your body better regulate blood glucose levels, also reduce your overall carbohydrate intake, replacing simple carbohydrates with complex carbohydrate foods. This means use whole flours and grains, beans, legumes, and fresh fiber-rich vegetables, rather than choosing to eat refined foods.
Eating five to six small meals a day, instead of the traditional three larger meals, can also help balance blood sugar levels and prevent excessively high insulin spikes after eating. In addition, a vegetarian diet high in organic vegetables and complex whole grains, along with small intakes of whole fruit that contains seeds or pits, rather than fruit juice, has also been found to be helpful for many people suffering from Type II diabetes.
Jerusalem artichoke is another food that can help diabetics control blood sugar levels. A diet rich in healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, extra virgin olive, raw virgin coconut butter and high lignin flax seed oil also supports you in maintaining level and stable blood sugar levels. ??Many Type II diabetes patients fare well on a diet that consist of 55 to 60 percent complex carbohydrates, 15 to 20 percent protein (with a minimum of 45 grams of protein per day), and 20 to 25 percent healthy fats.
In addition, you should increase your fiber intake to a daily level of 40 to 50 grams of fiber, with 10 to 15 grams of soluble fiber. High-fiber foods like beans and whole grains can be added slowly, perhaps at a rate of one serving per week, along with an increase in your intake of pure, filtered water.
Eating According to the Glycemic Index: Eating foods that have negligible impact on insulin levels can be especially important for people with diabetes. A scientific system of measurement known as the glycemic index was developed by researchers at the University of Toronto specifically for this purpose. Foods that have a high glycemic rating cause the greatest spikes in insulin levels, while foods with a low glycemic index are much more appropriate choices for diabetics because they do not produce significant impacts on insulin levels. By eating meals that contain an abundance of low-glycemic foods, you can significant improve your body’s ability to maintain low insulin and blood sugar levels.
Low-glycemic foods include raw, organic leafy green vegetables, fruits that contain seeds or pits, sweet potatoes, yams, organic whole-grains and whole grain breads, most legumes and nuts, yogurt, buttermilk, poultry, many types of fishes, and lean cuts of beef, bison, or lamb.
In general, cooked foods have a higher glycemic rating than raw foods.??Foods with a high-glycemic rating include white breads, bagels, English muffins, commercially packaged cereals, cookies, pastries, and most other desserts, raisins and dried fruits, white potatoes, whole milk and cheeses (both of which are high in lactose, a type of sugar), peanuts, peanut butter, and all processed flesh foods such as hot dogs and luncheon meats. Such foods are best avoided altogether.
Avoid Foods You Are Allergic To: Food allergies and sensitivities can exacerbate diabetes symptoms by causing inflammation. They can also destroy insulin-producing cells in the pancreas due to autoimmune reactions. The most common foods that trigger allergies for diabetics are wheat, chocolate, corn, milk and dairy products. Any food you are allergic to has the potential to aggravate a diabetic condition. Furthermore, it is important to note that any food can be an allergen. Therefore, if you are experiencing the tell-tale warning signs of diabetes you should be tested for food allergies.
Reliable allergy testing options include NAET, Kinesiology, Live Blood Cell Analysis, and electro dermal screening using computer-based technology provided by the Bio Meridian, Computron and others. These are all excellent, non-invasive options that offer direct accurate assessment and can be repeated when necessary without having to do traditional blood testing.??Leading allergy specialist William H. Philpott, M.D., of Choctaw, Oklahoma, has observed firsthand the effects of food allergies on Type II diabetes patients by studying blood sugar responses before and after test meals of single foods.
One of the most common responses of Type II diabetes patients when they ate offending foods was swelling of the body`s cells. Dr. Philpott found that, when the offending food was removed from a person`s diet, the diabetic reaction vanished. Treatment involves a four-day rotation diet that leaves out the offending food for three months. The food is then gradually reintroduced into the diet. If further negative reactions occur, however, the offending food should be eliminated from your diet altogether.
Energy Medicine: Dan Dunphy, PAC, has achieved great success in reversing both Type I and Type II diabetes in many cases by using electro dermal screening, which enables him to detect hidden microorganisms as well as interfering energy blockages that other forms of diagnostic tests are incapable of finding. Once these hidden, underlying causes are determined, other natural therapies can be employed to help patients recover.
Energy medicine devices, such as the Ondamed, can also be helpful in this regard.
Exercise and Stress Reduction: Regular exercise should be part of every diabetic’s daily routine. Exercise in combination with a weight loss program has been proven by the National Institutes of Health to reduce the odds of developing diabetes by 58 percent among people who are at risk for the disease. That is nearly double the rate of risk reduction achieved by people who take oral medications for their diabetes symptoms.
Exercise is extremely helpful for diabetes because of how it mimics the proper function of insulin to open the muscle cells for glucose to enter. Light exercise–which may include walking, swimming, bicycling, or any other of your favorite daily activities that result in a temporary increase in heart rate, as well as sweating–not only helps to control weight, but also helps to oxygenate tissues as well as lowering and stabilizing blood sugar levels.??
Caution: If you require insulin injections to manage your diabetes, be aware that exercising too strenuously can cause blood glucose to quickly drop to dangerously low levels, resulting in hypoglycemia. To prevent or counteract such a reaction, eat a fast-absorbing carbohydrate snack or drink a glass of orange juice.??
Herbal Medicine: Many herbs have blood sugar regulating properties and are therefore helpful in the management of glucose levels and non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Herbs that have been traditionally used include the Ayurvedic herb gymnesyl (Gymnema sylvestre), fenugreek seeds, huereque (derived from the root of a Mexican cactus), bilberry, bitter melon, garlic, Jerusalem artichoke, mulberry leaves, olive leaves, and ginseng. Heart and vascular tonics made from hawthorn berry and ginkgo biloba can also be useful.
Note: When taking herbs that lower blood sugar, it is important to monitor blood sugar and urine closely. Consult a skilled practitioner who can guide you in the use of herbs as part of a comprehensive diabetes management plan.??According to Dan Dunphy, the huerque cactus can significantly help to lower elevated blood sugar levels. So much so, that the majority of his insulin-dependent Type II diabetes patients were eventually able to discontinue taking insulin after they started supplementing with huerque. Dunphy points out, however, that after about six months most patients` start to develop a tolerance to huerque, which reduces its effectiveness. He recommends that patients stop using huerque for a month so that the tolerance wears off, and then start taking huerque again, repeating the month off process every four to six months from that point on.
For better results, he recommends that during the month off period, patients substitute their huerque use with nopal, another cactus-derived herb that also effectively reduces blood sugar levels. Both the huerque and nopal cactus in supplement form can be ordered through the Internet.??
Hydrotherapy: Hydrotherapy is the application of water, ice, steam and hot and cold temperatures to maintain and restore health. Treatments include full body immersion, steam baths, saunas, sitz baths, colonic irrigation and the application of hot and/or cold compresses. Hydrotherapy is effective for treating a wide range of conditions and can easily be used in the home as part of a self-care program. Many Naturopathic Physicians, Physical Therapists and Day Spas use Hydrotherapy as part of treatment. We suggest several at-home hydrotherapy treatments. Please seek the advice of your alternative health care practitioner before undergoing these procedures to make sure they are appropriate for you.
*Purified water is essential for any hydrotherapy treatment. The section Remedies for Treating Chlorinated Bath Water offers clear instructions and recommendations.
Juice Therapy: Helpful juice combinations for stabilizing blood sugar levels include a wide variety of vegetables. The combination of celery, cucumber, parsley, string beans, and watercress is excellent. Try any of the following combinations; in addition, experiment with your own. The key is to use primarily vegetables, use only the minimal amount of carrots or apple to sweeten your juice if at all. Try the following: celery, parsley and spinach; romaine lettuce, spinach and two carrots; cucumber, celery and chard. Drink a glass of any of the above combinations once or twice a day. Enjoy as a mid-day snack or with a handful of soaked almonds.
Nutritional Supplements: Important nutritional supplements for managing glucose and insulin levels include vitamin C, B-complex vitamins, and vitamin E, as well as the minerals magnesium, chromium, and zinc. Also useful are vitamin B6, biotin, magnesium, chromium, potassium, essential fatty acids, flaxseed oil, and vanadium, or vanadyl sulfate, an essential trace element with properties that mimic insulin. Other helpful supplements include alpha-lipoic acid, coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), amino acid complex, digestive enzymes such as protease, amylase, and lipase, and pancreatic enzymes.??Stabilized rice bran is another supplement that has recently been shown to provide significant benefits for managing diabetes because of its ability reduce and better regulate blood sugar levels.??
Note: While it is important to increase your dietary sources of nutrients, it is not always possible to do so. Older diabetics as well as diabetics who have problems with assimilation of nutrients should consult a physician about taking minerals and trace elements by intravenous infusion or transdermal (absorbed by the skin) delivery.??
Oxygen Therapy: The red blood cells in a diabetic`s blood have a reduced capacity to release oxygen because the vital delivery molecule 2,3-diphosphoglycerate is in short supply. The 2,3-diphosphoglycerate molecule plays a key role in stimulating red blood cells so that they properly deliver oxygen to the body`s cells, organs, and tissues. Insufficient amounts of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate inhibit the body`s ability to deliver enough oxygen to the areas where it is needed. Because many diabetic health complications, especially the risk of gangrene and other infections, result from oxygen depletion in body tissues, it is critical to deliver oxygen to those depleted tissues. Practitioners using oxygen therapy with ozone (a more reactive form of oxygen) have seen remarkable improvements, including increase in 2,3-diphosphoglycerate, in both major and secondary problems associated with Type II diabetes.
Hydrogen peroxide therapy can also be helpful for Type II diabetic patients. The late Charles Farr, MD, a leading expert in the use of hydrogen peroxide therapy, achieved many successful outcomes with Type II diabetes patients by administering intravenous solutions of hydrogen peroxide. Dr. Farr reported that his best results were accomplished with patients who had never been treated with insulin therapy or any form of diabetes drug, in which case he was often able to completely reverse their condition.??Another benefit of oxygen therapy is the enhanced levels of the energy transport molecule adenosine triphospate (ATP), which maintains cell membrane integrity and is essential for creating energy at the cellular level.
Stress Reduction: Because the effects of chronic stress lead to elevated blood sugar levels, you need to incorporate relaxation and rejuvenation techniques into your daily routine. Some of the mind/body techniques that are shown to be helpful to diabetics are yoga, meditation, guided imagery, and biofeedback training. Receiving massages and/or bodywork is also helpful. Try different techniques, evaluate the outcomes with your practitioners, and choose the approaches that work best for you.
Topical Treatment: To improve your body`s circulation use dry brush massage daily. Doing so can help glucose move from your bloodstream into the cells, where it is used as an energy source.
Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM): Aspects of TCM that have been found helpful in treating diabetes include acupuncture and a combination of herbs. The TCM approach is most effective with beginning and intermediate Type II diabetes and very early Type I diabetes. TCM is also effective in slowing down the process of neuropathy and improving circulatory problems. Acupuncture treatments focused on the spleen/pancreas can reduce the autoimmune reaction, as well. In addition, acupuncture can also help to improve overall function of the endocrine system, thus helping to prevent or reverse symptoms of diabetes that are aggravated by hormonal imbalances.??Chinese herbs can also help ease diabetic symptoms. Among the most useful herbs for this purpose are astragalus, rehmannia, and wild yam.
Alternative Professional Care The following therapies can also be useful for testing or treating diabetes: Biofeedback Training and Neurotherapy, Bio-Energetic testing, Detoxification Therapy, Guided Imagery, Magnetic Field Therapy, Massage Therapy and other body work techniques, Mind/Body Therapies, Osteopathic Medicine, Reflexology, Qigong, Tai Chi, and Yoga.
Quick Action Plan for Diabetes
1. Be aware for early signs of blood sugar problems. Have the proper yearly tests performed.
2. Keep in mind that the goal of diabetic treatment and self-care is to restore blood sugar levels close to normal and to correct related metabolic disorders. One of the best ways to accomplish this is by eating small, frequent meals throughout the day that emphasize fresh, organic foods that are low on the glycemic scale, such as raw and lightly steamed vegetables, low sugar whole fruits, nuts, seeds, whole grains and legumes, yams, wild fish, poultry, lean cuts of beef, bison meal lamb or veal.
3. Minimize or eliminate your intake of simple carbohydrates and all sugars, as well as tobacco and processed “junk foods.” In addition, reduce your intake of alcohol and caffeine. Both alcohol and caffeine could be enjoyed on special occasions, rather than daily or even weekly habits.
4. Remain hydrated; drinking adequate quantities of pure water is essential for all aspects of your health.
5. Engage in regular light exercise and stress reduction because they are keys to maintaining lower levels of blood sugar.
6. Consider supplementing with nutrients such as B-complex vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin E, chromium, magnesium, potassium, essential fatty acids, CoQ10, alpha lipoic acid, and vanadium. Stabilized rice bran supplements can also be helpful.
7. Herbs such as astragalus, bitter melon, fenugreek, garlic, ginseng, Gymnema sylvestre, and huerque can also provide significant benefits.
8. If you have already developed Type I or Type II diabetes, combine the above self-care natural cures with professional care from a holistically oriented physician or other alternative health care practitioner. Particularly useful professional care therapies for treating and preventing diabetes include chelation therapy, food allergy testing, parasite testing and if necessary, cleansing, oxygen therapy, and professional dietary and nutritional counseling. Ayurveda and traditional Chinese medicine can also be helpful.
9. Prevention, if you are pre-disposed and managing a diabetic condition, is a life-long commitment. By committing to the guidelines above, you can significantly improve your symptoms, and, if you suffer from Type II diabetes, quite possibly reverse them altogether. Implementing diet and lifestyle changes can help improve your energy levels, and your confidence in your ability to experience greater health.
Rife and Zapper Frequencies: Diabetes Type 1 Frequency 429.70 for 1-2 hours per day
Diabetes Type 2 Frequency 465.00 for 1-2 hours per day
Diabetes Type 3 Frequency 787.00 for 1-2 hours per day
Diabetes Gestational: 0.15, 0.89, 12.70, 77.00, 134.20, 235.87, 312.50, 420.35, 465.30, 872.90,
Diabetes Insulin-Dependent: 0.15, 0.89, 1.70, 6.97, 12.89, 62.30, 429.70, 478.23, 895.00, 951.30